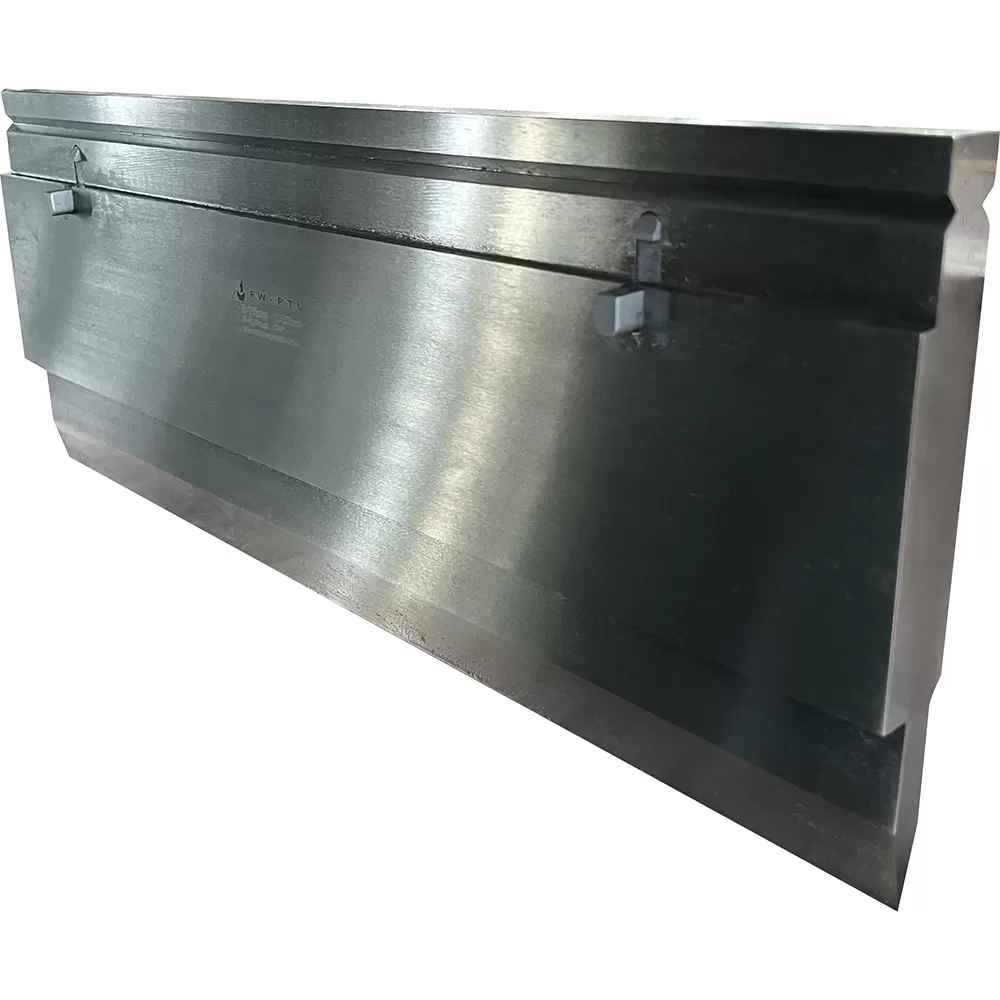

PARAMETER
Design principle of press brake tooling
1. Basic structure and working principle of the mold:
-Basic structure: The press brake tooling is usually composed of an upper die (punch) and a lower die (die). The upper mold is used to apply pressure, while the lower mold is used to support the material and form the required bending angle.
-Working principle: The press brake causes plastic deformation of the metal plate under the action of force through the relative motion of the upper and lower molds. The upper mold is pressed downwards, and the metal plate is bent into the desired angle and shape.
2. Classification of press brake tooling:
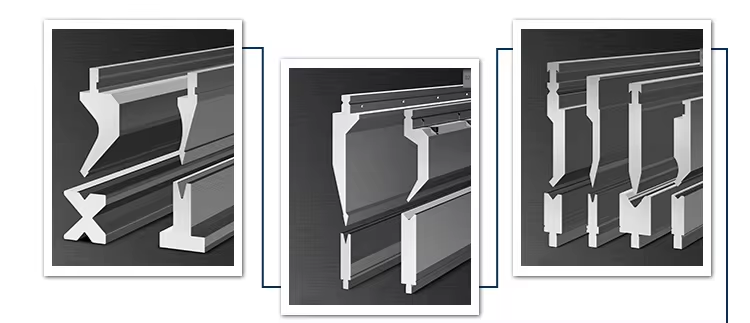
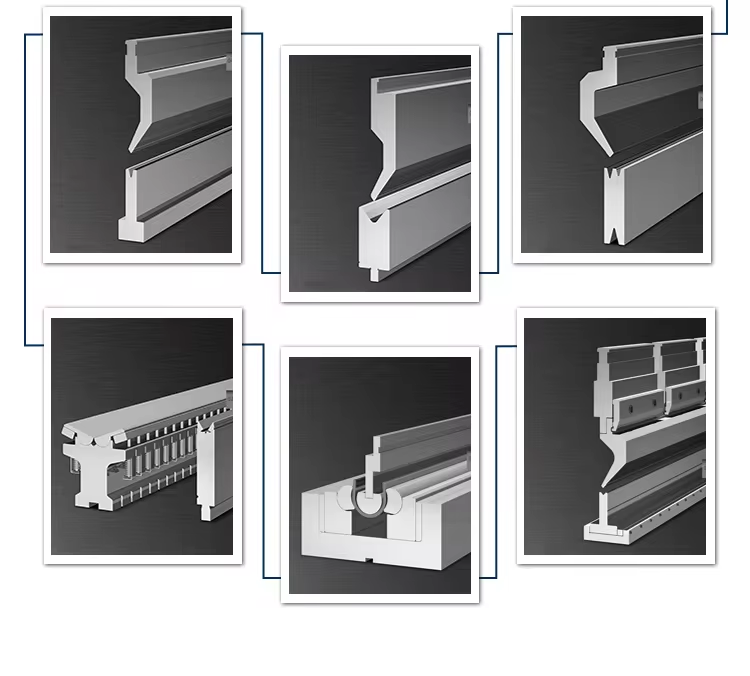
-V-shaped mold: commonly used in press brakes, the groove of the mold is V-shaped and can bend materials of various thicknesses.
-U-shaped mold: The mold groove is U-shaped and suitable for materials that require a larger bending radius.
-Air bending mold: used for bending lightweight materials, which can reduce material deformation during the bending process.
-Rectangular mold: suitable for occasions with specific requirements for bending angles.
3. Mechanical analysis in mold design:
-Stress analysis: Analyze the stress situation of the mold and material during the bending process to ensure that the mold design is strong enough to withstand working pressure.
-Strain analysis: Analyze the deformation of materials during the bending process to optimize bending parameters and reduce material waste.
-Material selection: It is necessary to choose suitable mold materials to ensure the wear resistance and stability of the mold. Common choices include high-strength steel and alloy steel.
Material selection for press brake tooling
1. Performance requirements for mold materials:
-Hardness: Mold materials need to have sufficient hardness to withstand long-term mechanical pressure and wear.
-Wear resistance: The mold is subject to friction during use, so it is required that the material has good wear resistance.
-Corrosion resistance: In certain environments, molds may be exposed to corrosive media, so corrosion resistance is also important.
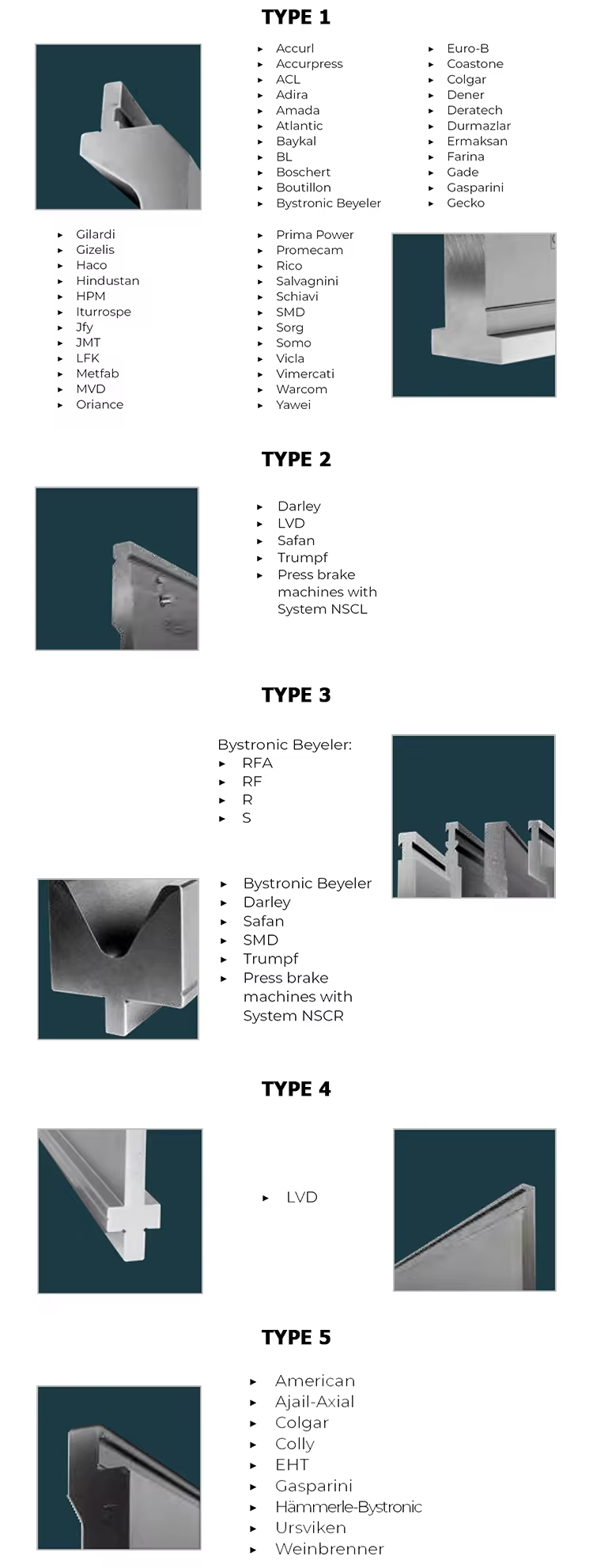
2. Comparison and selection principles of commonly used materials:
-High speed steel (HSS): It has good hardness and wear resistance, but is expensive and suitable for molds with high strength requirements.
-Alloy tool steel (such as D2, SKD11): It has excellent comprehensive properties, including wear resistance, toughness, and hardness, and is suitable for use in most press brake tooling.
Manufacturing and processing of molds
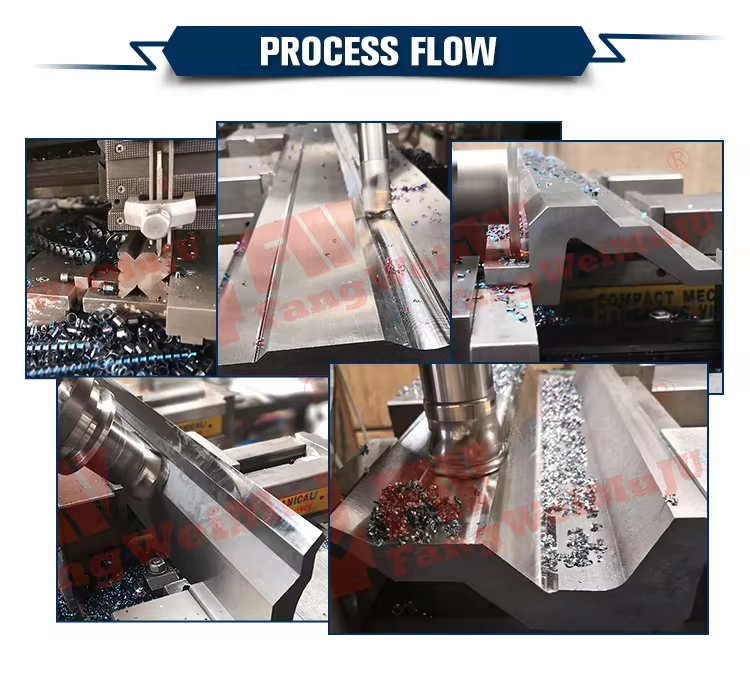
1. Process of mold processing:
-Rough machining: including removing most of the excess material to form the initial shape of the mold. The commonly used methods are milling and turning.
-Precision machining: Fine machining is performed on the rough machined mold to improve its accuracy and surface smoothness. Common methods include grinding and electrical machining.
2. Selection of processing equipment and control of processing accuracy:
-CNC machine tools: improve machining accuracy and repeatability, suitable for molds with complex shapes.
-Laser cutting: used for cutting high-precision and complex shapes.
3. Application of advanced manufacturing technology:
-Laser cutting: It can accurately cut mold materials and reduce waste.
-CNC machining: providing high-precision and high-efficiency machining solutions.
Optimization of bending process
1. Parameter optimization during bending process:
-Bending angle: Optimize the bending angle to achieve the best bending effect.
-Bending speed and pressure: Adjust the bending speed and pressure to reduce material deformation and improve production efficiency.
2. The influence of mold design on bending accuracy:
-Mold geometry: affects the accuracy and consistency of the material after bending.
-Mold fitting accuracy: affects the uniformity of material stress during the bending process.
Maintenance and repair of press brake tooling
1. Common faults and repair methods of molds:
-Wear and tear: Regularly inspect and grind the surface of the mold.
-Fracture: Repair cracks in the mold or replace damaged parts.
2. Strategy for extending the lifespan of molds:
-Regular maintenance: Keep the mold clean and perform regular maintenance.
-Reasonable use: Avoid overloading the mold and ensure that it works within the design parameter range.
Practical application cases
1. Design and application examples of press brake tooling in specific industries or applications:
-Automotive manufacturing industry: press brake tooling are used for the production of body components such as car doors and chassis.
-Electronics industry: used for producing casings and brackets for electronic products.
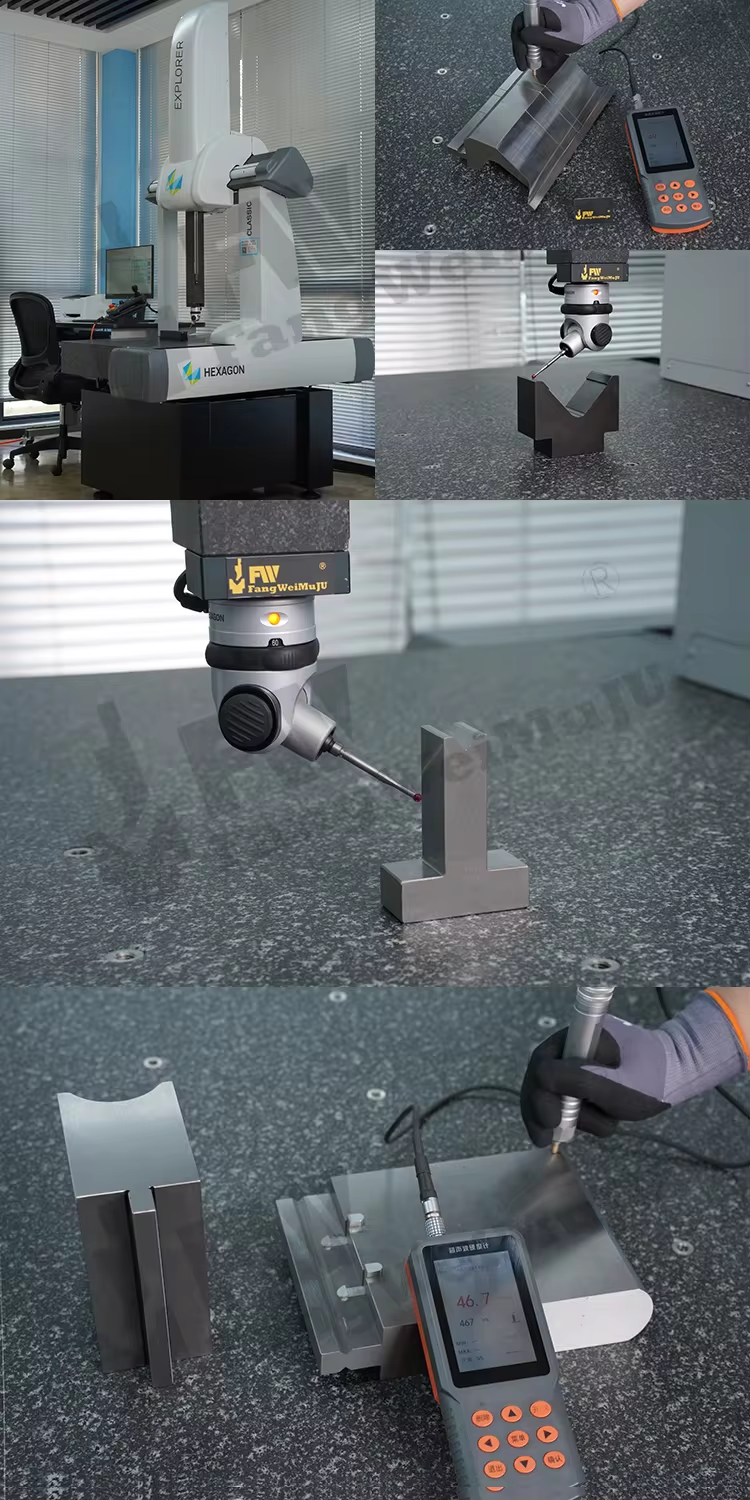
2. Relevant performance testing and result analysis:
-Test content: Conduct performance tests on the mold, including bending accuracy, wear resistance, and service life.
-Result analysis: Analyze the performance of the mold through test data and make improvements to the design.
We hope these detailed information can help you better understand and design press brake tooling. If you have any further questions or need specific technical details, please let me know at any time!















Anhui Hisman Intelligent Equipment Manufacture Co., Ltd. is located in A-8#,Dahe Industrial Park,Bowang Town, Bowang District,Maanshan City,Anhui Provence,China.
Tel: +86 19955505001
Email: info@ahhisman.com
Fax: +86 0555 6765 075
Phone: +86 138 5551 1880
Add: A-8#, Dahe Industrial Park, Bowang Town, Bowang District, Maanshan City, Anhui Province, China
INQUIRY